Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic disease that occurs when your body’s immune system attacks your own tissues and organs. Pain and inflammation caused by systemic lupus erythematosus can affect many different body systems such as your joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, brain, heart and lungs. People of all ages can get lupus, but 9 out of 10 adults with the disease are woman between the ages of 15 and 45.
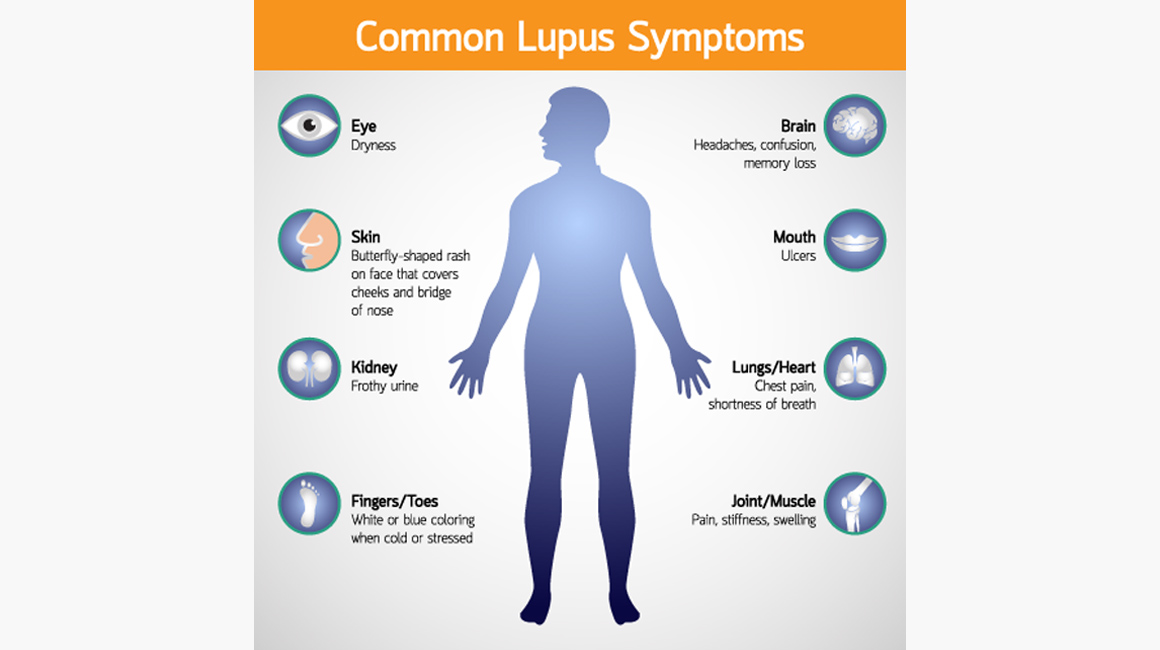
Symptoms
The symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus are different for each person. These symptoms can be mild or severe and may include one or more of the following:
- A red rash across the cheeks and nose
- Small, painless sores in the roof of the mouth or in the nose
- Arthritis, especially in the hands and feet
- Lower amounts of red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets in the blood
- Inflammation in the lining of the lungs or heart, which causes chest pain when lying down or taking deep breaths
- Decrease in kidney function, which can cause swelling of the feet and legs
- Problems with the brain or nervous system, which can cause abnormal thoughts, seizures, memory and concentration problems as well as many other symptoms
Causes
The causes of systemic lupus erythematosus are unknown. Genetics factors interacting with something in the environment may predispose you to lupus. There are certain triggers for lupus such as sunlight, medications and infections.
Treatment
Treatments involves suppressing the overactive immune system and ultimately inducing remission and preventing organ damage with medications and lifestyle changes. Rheumatologists treat systemic lupus erythematosus with medications aimed at controlling inflammation and minimize disease activity so that no long-term organ damage occurs.
Opening Hours
Monday – Thursday: 7:30AM to 4:30PM
Friday: 7:30AM to 3:30PM
Saturday – Sunday: Closed

